강화학습이란:
Agent가 특정 environment에서 reward를 많이 쌓을 수 있는 방향으로 action을 취하는 것
(방법을 알려주는 것은 강화학습이 아님)
→ 방법을 알려주지 않으므로 초기에 불필요한 학습 과정이 많아짐
→ 우연에 의해서 random action을 취하게 되고 그 때 reward를 얻게됨
강화학습이 잘 적용되는 분야
반복적으로 작업할 수 있는 것들
- 바둑
- 자율주행 (강화학습 뿐만 아니라, 세팅값들에의해서 같이 조절됨)
너무 가까워 지면 멈추라는 세팅값들이 존재함
강화학습이 잘 적용되지 않는 분야
변동성이 많은 것
- 주식
- 로또번호 예측
강화학습 알고리즘 Basic
1) The agent interacts with the environment by performing an action.
→ agent가 action을 취하면서 환경과 interaction을 함
2) By performing an action, the agent moves from one state to another.
→ agent가 action을 취하면 다음 state로 이동
3) The agent receives a reward based on the action it performed.
4) Based on the reward, the agent understands whether the action is good or bad.
→ 받은 reward를 통해 취한 action에 대한 판단을 함
5) If the action was good, that is, if the agent received a positive reward, the agent will prefer performing that action, else the agent will try performing other actions in search of a positive reward.
RL의 5가지 기본용어
• Agent : a software program that learns to make intelligent decisions
e.g.) chess player, Mario in a Super Mario Bros. game.
• Environment : the world where the agent stays within
e.g.) chess board, the world of Mario
• State : a snapshot of moment in the environment (including the agent.)
e.g.) In a 3x3 grid world, the player can be in 1 of the 9 locations. Each location of the player is a state.
• Action : a move performed by the agent.
e.g.) Moving to a new location in the grid world, moving a chess piece in a chess board
• Reward : a feedback given for an action
e.g.) taking opponent's chess piece, reaching a goal

Markov property:
미래의 상태는 현재의 상태에 의존됨(과거의 상태는 관여하지 않음)
– "Future depends only on the present and not on the past."
– a memoryless property
Markov Chain을 표현하는 2가지 방법 (state, transition prob.)
1. State diagram

2. Transition matrix

Markov Reward Process (MRP)
Reward가 추가된 Markov chain의 확장판
• Markov Chain = states + transition probability
• Markov Reward Process = states + transition probability + reward function
– States: s
– Transition probability: P(s' | s)
– Reward function: R(s)
Reward function
: A reward function defines reward obtained in each state
E.g.) reward in state cloudy, reward in state windy, reward in state rainy
[Markov Decision Process (MDP)]
• Markov Decision Process = states + transition probability + reward function + actions
– States: s
– Actions: a
– Transition probability: P(s' | s, a)
s에서 a액션을 취하여 s'으로 이동할 확률

– Reward function: R(s, a, s')
s에서 a액션을 취하여 s'으로 이동했을 때 얻는 reward
목표하는쪽으로 reward를 제공하는 것이 중요함
Two types of action spaces
1. 이산적 action space → categorical policy로 표현
2. 연속적 action space → gaussian policy로 표현
Policy: difines the agent's behavior in an environment
When the agent first interacts with the environment, it uses a random policy
| States | actions |
| A | right |
| B | right |
| C | down |
| D | down |
2가지 Policy: Deterministic vs. Stochastic Policy
Deterministic policy의 notation: Mu
stochastic policy: 확률적으로 action에 대해 정하는 것
> notation: Pi
stochastic policy에서
action space가 discrete할 때는 categorical policy로 표현

action space가 continuous할 때는 gaussian policy로 표현
episode ≒ trajectory (표현방법을 sequence로 표현한 것)
> notation: Tau
Episodic Task vs. Continuous Task
- Episodic task: 한 판 끝났다고 표현할 수 있는 것
- Continuous task: terminal state가 없음
eg) 개인 비서 로봇
Horizon
- Finite horizon : episodic task와 유사
- Infinite horizon: continuous task와 유사
Return(중요!)
각 episode의 총합 = return
** reward는 각 episode별 reward임
> R(tau)로 표현
** continous할 때는 reward가 양수이면 무한대로 증가하게됨
0< gamma < 1 사이의 특정 값을 지수배 해줌

Small Discount Factor vs. Large Discount Factor
큰 gamma값을 넣어주면 future reward에 초점을 맞추는 것임
gamma값을 작게하면 immediate reward에 더 많은 reward를 적용
> task의 성향에 따라 gamma값을 적절히 조절해줘야 함
Value Function
V(s) : S state일 때의 value
> V(2): 2를 초기로 시작했을 때의 value

** Pi는 stochastic policy

value function with stochastic policy인 경우
expected return을 사용함
eg) A일때만 확률적으로 이동한다고 했을 때

The optimal value function V*(s)

Q function
Q(s, a): state S에서 action a를 취했을 때의 value
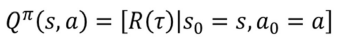

Vtau(S)와 Qtau(S)의 차이점
Qtau(S)는 action a1, a2에 따라 달라짐
Vtau(S)는 action a1, a2의 평균 값임
Q-table & optimal policy

Model-based Learning vs. Model-free Learning
Model-based Learning: 바둑과 같이 state와 environment가 정해짐
Model-free Learning: 해보기 전까지는 모름
> transition probability를 추정해야함 (몬테카를로 법칙)
Episodic vs. Non-episodic environments
Episodic: agent의 current action이 미래에 영향을 주지 않는 것, FrozenLake
Non-episodic environments: 체스와 같은 것
Single vs. Multi-agent environments
Single: agent가 1개일 때
Multi-agent environments: 로봇축구
Fully Observable vs. Partially Observable environments
Partially Observable environments: 일부의 환경만 보여주는것(스타크래프트)
Static vs. Dynamic environments
Static : 내가 action을 취하지 않으면 agent가 가만히 있는 것
'IT > 강화학습' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Temporal Difference Learning (0) | 2022.10.25 |
|---|---|
| Monte Carlo methods - Importance Sampling (0) | 2022.10.12 |
| Monte Carlo methods (0) | 2022.10.11 |
| Bellman equation 정리 (0) | 2022.09.27 |
| Frozen Lake 구동해보기 (0) | 2022.09.17 |